
Top 5 RPO Models in Recruitment
24/07/2022
Understand The Difference Between RPO and Staffing
23/08/2022- What Is a Payroll Structure in India?
- Why Does Payroll Structure Matter for Businesses and Employees?
- What Are the Fixed and Variable Components of Payroll?
- How Does the New Wage Code 2026 Affect Payroll Structure?
- How to Create an Ideal Payroll Structure for Your Organization?
- What are the Different Types of Payroll Structures?
- What are the Different Components of Payroll Structure?
- Factors to Consider for Payroll Structure
- What Are the Benefits of an Optimized Payroll Structure?
- What Are the Common Payroll Mistakes and How to Avoid Them?
- What are the Statutory Compliance Requirements of Indian Payroll?
- Why should you Outsource Payroll Functions?
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A payroll structure covers all details of the compensation offered to an employee with a complete break-up of the components. Any change to this payroll structure has a major effect on the tax exemptions that can be claimed by the employee.
Every HR or payroll department in an organization is always tasked with creating a solid pay structure for the employees. It is important to have an understanding of what constitutes the salary earned. This is especially necessary to make well-informed decisions on savings, investments, or tax exemptions that can be claimed.
The payroll structure of a company is categorized under three main heads: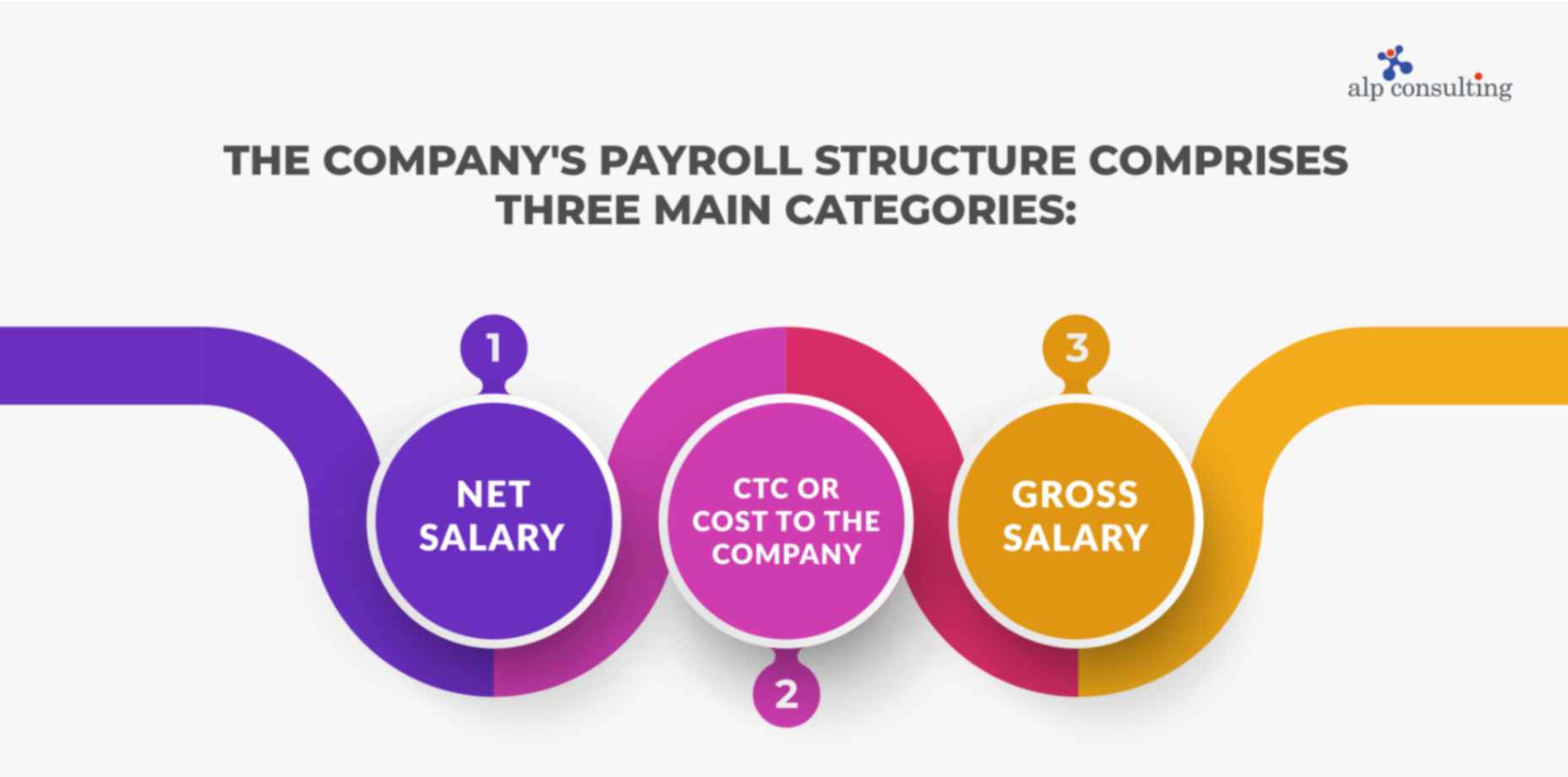
What Is a Payroll Structure in India?
A payroll structure in India is essentially a framework or breakdown of an employee’s total salary package that includes elements like earnings deductions, benefits, etc, that is assimilated and forms the net salary. Let us look at the structure:
1. Net salary
The take-home amount after the deductions. The deductions in the Indian payroll system can include elements like Provident Fund (PF), Employees’ State Insurance (ESI), Labour Welfare Fund, National Pension Scheme (NPS), Professional Tax, etc.
2. Gross salary
This will be the employee’s total earnings without deductions and what will be shown on the payslip. Elements like the basic salary, allowances, and tax are added up to get the gross salary. It includes overtime pay, bonuses, holiday pay, and more.
3. CTC or Cost to the Company
The total monetary benefits that the employer gives to the employee for the whole financial year. CTC is the full salary package of the employee and not the take-home salary. It comprises all monthly additives like “Basic Salary,” “Perquisites,” and “Allowances”.
Fixed & Variable Pay in Payroll Structure
The salary structure of an employee can have both fixed and variable elements. Fixed pay is what is paid to the employee by the employer in the form of a fixed monthly salary. This is the accrual salary that is shown on the salary slip with basic and multiple allowances. The variable pay or the extra incentives is not given every month.
All companies have different policies for this. Fixed pay could include basic pay, dearness allowance (DA), house rent allowance (HRA), conveyance allowance, other special allowances, etc. Whereas the variable pay is paid out based on employee or company performance like when the company meets revenue targets or as a commission of sales achieved by the employee.
|
Category |
Component |
Description / Purpose |
|
A. Earnings (Income Components) |
Basic Salary |
Fixed core salary; forms the basis for PF, gratuity, and other benefits (35–50% of CTC). |
|
Dearness Allowance (DA) |
Compensation for inflation and cost of living (mostly in the public sector or manufacturing). |
|
|
House Rent Allowance (HRA) |
Paid to meet housing expenses; partially exempt from income tax under Section 10(13A). |
|
|
Conveyance / Travel Allowance |
Covers commuting or travel-related expenses. |
|
|
Medical Allowance / Reimbursement |
For medical expenses, a tax benefit is available if reimbursed with bills. |
|
|
Special Allowance |
Balancing figure; varies by company policy, often fully taxable. |
|
|
Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) |
Reimbursement for travel within India during leave; tax-exempt under conditions. |
|
|
Bonus / Incentives |
Performance or productivity-based payments may be monthly, quarterly, or annual. |
|
|
Gross Earnings |
Total of all earning components before deductions. |
|
|
B. Deductions |
Employee Provident Fund (EPF) |
Employee contribution (12% of Basic); mandatory under EPF Act, 1952. |
|
Employee State Insurance (ESI) |
0.75% of Gross Salary (for employees earning ≤ ₹21,000/month). |
|
|
Professional Tax (PT) |
State-imposed tax; applicable in states like Maharashtra, Karnataka, and West Bengal. |
|
|
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) |
Income tax withheld by the employer based on the employee’s tax slab. |
|
|
Loan / Advance Recovery |
Deduction for any salary advances or company loans taken by the employee. |
|
|
Total Deductions |
Sum of all statutory and voluntary deductions. |
|
|
C. Employer Contributions (Benefits) |
Employer’s Provident Fund Contribution |
Employer’s share (12% of Basic Salary) contributed to EPF. |
|
Gratuity |
Statutory benefit for employees completing 5+ years; 4.81% of Basic. |
|
|
Employee State Insurance (ESI) |
Employer’s share (3.25% of Gross Salary) if applicable. |
|
|
Health / Life / Accident Insurance |
Group insurance or wellness benefits are offered by the employer. |
|
|
Pension / NPS Contribution |
Employer’s contribution toward retirement or pension schemes. |
|
|
Other Fringe Benefits |
Meal coupons, travel allowance, mobile reimbursement, etc. |
|
|
D. Salary Calculations |
Gross Salary |
Total earnings before deductions. |
|
Net Salary (Take-Home Pay) |
Gross Salary – Deductions. |
|
|
CTC (Cost to Company) |
Gross Salary + Employer Contributions. |
According to reports, the average annual base salary per employee in India is about ₹9,45,489 (≈ ₹78,790 per month) in 2024.
Why Does Payroll Structure Matter for Businesses and Employees?
A well-designed payroll structure is not only beneficial for employers but is also advantageous for employees. It is a system that drives a fair, transparent, and efficient compensation management program, enhancing the overall operational efficiency.
For Businesses:
- A properly crafted payroll system ensures that companies will regularly adhere to the Indian labour laws and taxation policies.
- A clear payroll structure enables companies to plan their finances and budget accurately.
- A standardised system creates a fair and transparent process, organizing salary calculations, tax deductions systematically.
- Authentic payroll data offers support in crafting robust HR strategies, as it provides detailed information about components like labour expenses, turnovers, etc, enabling HR departments to make smart and informed data-powered decisions.
For Employees
- Employees understand their salary systems clearly with a payroll system that is properly structured. They will have a good idea about their deductions, benefits, etc.
- A regulated and structured payroll system also enables employees to enhance their tax efficiency.
- A well-designed and defined payroll structure elevates the financial security of employees, along with boosting their morale and trust.
- A clear payroll framework will also provide a clear picture to employees about how their performance status, promotions skill upgrades are affecting their salary progress.
What Are the Fixed and Variable Components of Payroll?
|
Basis of Comparison |
Fixed Components |
Variable Components |
|
Definition |
Fixed components are the guaranteed and consistent parts of an employee’s salary that do not change month to month. |
Variable components are performance-based or conditional payments that may fluctuate based on results, targets, or company performance. |
|
Nature of Payment |
Paid regularly and uniformly every month, regardless of performance or business results. |
Paid irregularly or periodically, depending on performance, incentives, or project outcomes. |
|
Examples |
– Basic Salary – Dearness Allowance (DA) – House Rent Allowance (HRA) – Conveyance Allowance – Medical Allowance |
– Performance Bonus – Sales Incentives – Commission – Overtime Pay – Profit Sharing – Project Completion Bonus |
|
Stability |
Stable and predictable, it forms the backbone of the salary structure. |
Fluctuates based on individual, team, or organizational performance. |
|
Tax Treatment |
Generally taxable but may include certain exemptions (e.g., HRA, LTA). |
Fully taxable, as they are linked to additional earnings. |
|
Impact on Statutory Contributions |
Used to calculate statutory benefits like PF, ESI, Gratuity, and Bonus. |
Typically not included in statutory benefit calculations. |
|
Purpose |
Ensures financial stability and security for employees. |
Encourages higher performance, productivity, and motivation. |
|
Dependence on Performance |
Not performance-linked; paid regardless of results. |
Directly tied to performance metrics or business outcomes. |
|
Frequency of Payment |
Usually paid monthly. |
Paid monthly, quarterly, or annually (depending on company policy). |
|
Percentage of Total Salary (Approx.) |
Forms 60–80% of the total salary (CTC). |
Forms 20–40% of total salary (CTC), depending on industry and role. |
How Does the New Wage Code 2026 Affect Payroll Structure?
The New Wage Code is likely to be rolled out in 2025-26. The states are expected to finalize the rules before it is implemented. The Indian Government is expected to replace 29 existing labour laws
Here are some of the key effects of the new wage code:
1. Emphasis on the Universal minimum wage
The new wage law will focus on a universal wage system that will be applicable to all employees across sectors. The system will be set by the central government based on the floor wage.
2. Enhanced Social Security
The new code will extend social security advantages to all workers that entail unorganized, gig workers, etc. Benefits like Provident Fund, Employees’ Pension Scheme, and insurance coverage will be extended to all.
3. Working Hour Relief
The code is likely to set the maximum work week to 48 hours. In case workers work overtime, then they must be paid at a rate of at least double the regular rate.
4. Gig and Platform Workers
The new code will also make registration mandatory for gig and platform workers and will mandate their contribution to social security schemes.
5. Focus on Gender Equality
The new law will eliminate the possibility of gender inequality by prohibiting discrimination in salary, hiring, and working conditions.
6. Fixed-term Contracts
The rights of the fixed-term employees will be clarified by the new wage code, ensuring that they are provided with the same benefits as permanent employees.
7. Implementation in Phases
The new wage code is likely to be rolled out in phases, ensuring businesses adapt easily.
How to Create an Ideal Payroll Structure for Your Organization?
To craft an ideal payroll structure, companies need to focus on certain elements, like:
Set up a comprehensive payroll policy- This will involve giving a definitive structure to salary components, setting up of payroll schedule, highlighting deductions and withholdings. Establish error correction systems, etc.
Ensure adherence to compliance and legal aspects- Companies must follow rules and regulations laid out by government bodies and handle tax implications.
Design salary and compensation structures- Select a structure that caters to business needs and decide on pay grades for different company positions.
Choose and implement a payroll system- Companies must select a reliable system that adheres to the manpower requirements, growth plans, and tax obligations.
What are the Different Types of Payroll Structures?
Companies have the freedom to choose the best salary structure that is ideal for them. This is dependent on factors like industry type, business size, or even business location. The three types used are traditional, broadband, and market-based. The most commonly used type is market-based structure.
In the traditional structure, the salary is divided into many pay grades with a maximum and minimum salary range set for each employee group. Key metrics like performance or employment tenure can be used to fix a pay hike. The more flexible broadband structure uses lesser pay grades so the salary range can get higher. Due to the possible instances of pay disparities, this salary structure type is not very popular among companies.
The market-based salary structure is almost like a combination of traditional and broadband structures but the pay is determined based on the market range for each position. Market data is collected with some research on what other similar companies are paying their employees.
What are the Different Components of Payroll Structure?
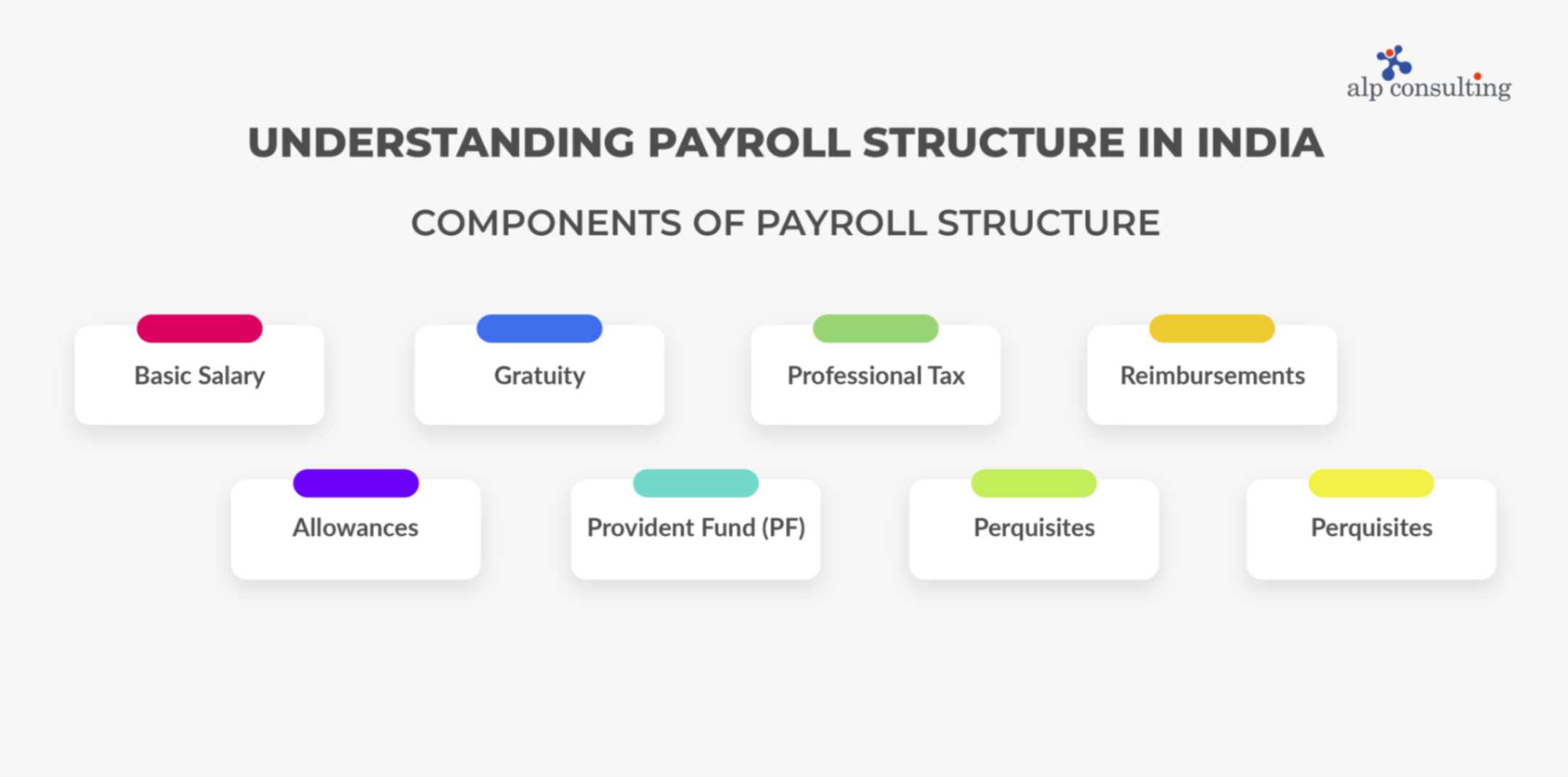
1. Basic Salary
This is the taxable base income of an employee based on the designation and industry they work in. It ideally constitutes 35% to 50% of the total salary.
2. Allowances
Fully or partly taxable amount paid to the employee as part of their regular duty like Dearness Allowance, Travel Allowance, House Rent Allowance, Conveyance Allowance, Medical Allowance or Leave Travel Allowance.
3. Gratuity
An essential lump sum benefit payable by the employer after completion of 5 years or more of service.
4. Provident Fund (PF)
Based on the employee benefits scheme of the payroll salary structure in India PF includes investments made by both employee and employer.
5. Professional Tax
It is an amount deducted from the income of salaried people, and it is paid to the state government.
6. Perquisites
Non-cash benefits, such as Profit sharing, Stock options, Fringe benefits, etc. are enjoyed by some employees based on their position in the company.
6. Reimbursements
This includes the various types of reimbursements that employees are offered like phone bills, medical treatments, office stationery and newspaper bills, etc. It is not included in the pay but reimbursed after bills are submitted by an employee.
7. Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC)
A state insurance scheme is required to be availed by the company if there are 10 or more employees.
Factors to Consider for Payroll Structure
The payroll structure should always align with the business’s vision and goals. An optimized payroll structure can greatly enhance the overall effectiveness of the company’s reward strategies.
There must be an ideal balance between the internal and external market in the company’s overall pay structure. If a company is consistently behind in the external market with respect to pay scales, then this needs to be addressed. Whereas if some companies are regularly considered paymasters or employers of choice, the base salary is not always driven by the external market data.
Identifying job families based on your company’s reward strategy can help ensure that the payroll structure differentiates pay premiums for certain skill sets or business-critical areas. This helps greatly when it comes to attracting and retaining the best talent. Also, consider the pay grade width you want to follow for each grade level of employees. Wider grades can give you more flexibility in managing pay and reduce implementation costs as well.
What Are the Benefits of an Optimized Payroll Structure?
An optimised payroll system enhances business operations. Boosts employee satisfaction and ensures a healthy working structure. Let’s find out what some of the benefits are:
1. Employee-centric Advantages
It improves employee experience and satisfies them as payments and benefits are made on time, reducing room for errors. They are offered a chance to manage their own payroll-related data and information through self-service portals.
2. Financial and Operational Advantages
A systematic payroll structure diminishes the chances of errors in calculations. This results in cost efficiency and saves time. The automatic structure of payroll allows businesses to focus on other strategic functions. It also reduces legal and compliance risks.
3. Competitive Benefits
The usage of modern technology and data analytics in designing payroll structures gives an extra edge to businesses, as they can smoothly track labour expenses, identify trends, and make smart and intelligent business decisions.
What Are the Common Payroll Mistakes and How to Avoid Them?
Some of the common payroll errors are:
- Lack of clear communication
- Calculation errors
- Tax errors
- Insufficient record keeping
- Misclassifications
- Inconsistent and inaccurate data
To avoid these common mistakes, companies must follow these steps:
- Utilize modern payroll software to automate processes, diminishing human error and saving time and cost.
- Integrate and implement systems where employees can automatically update their data accurately. Businesses must monitor and run from time to time to detect errors.
- Update and analyse the payroll system regularly to comply with the new state central laws and regulations.
- Create and set clear and comprehensive policies in payroll to manage sudden changes in employee salaries and compensation structures.
- Safeguard sensitive payroll data from being attacked by security breaches by creating robust security frameworks.
What are the Statutory Compliance Requirements of Indian Payroll?
Before handing out the offer letter to a newly appointed candidate, employers must make sure that the salary structure includes all the important components. It is extremely crucial to maintain a payroll structure that has statutory compliance.
All the labor and taxation laws of the state come under statutory compliance, and so does the payroll structure. In India, every company has to mandatorily adhere to both national and state-level laws. Companies dealing with statutory compliance need to be well-versed in the various labor regulations in India.
Indian payroll statutory compliance entails elements like deducting and remitting TDS (Tax Deducted at Source), making contributions to social security schemes like Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF) and Employees’ State Insurance (ESI), and adhering to state-specific requirements like Professional Tax and Labour Welfare Fund. Key laws also govern payments (Minimum Wages Act), gratuity, and bonus payments, as well as workplace conditions through the Shops and Establishments Act.
Why should you Outsource Payroll Functions?
Creating a salary structure that offers both financial and tax benefits is the key to successful payroll processing and reporting. Outsourcing the key payroll processing functions to experts like Alp Consulting ensures:
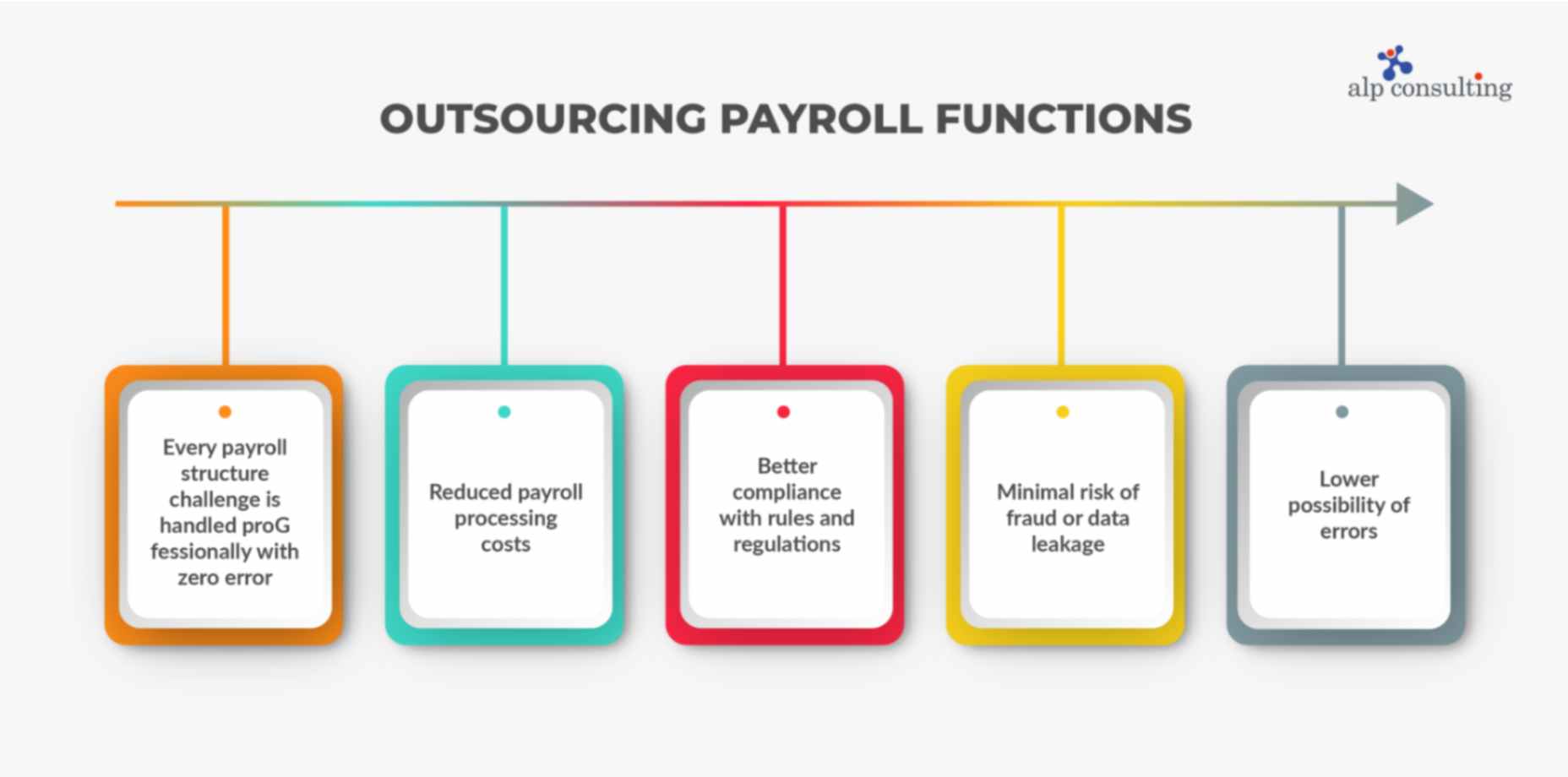
- Every payroll structure challenge is handled professionally with zero error
- Reduced payroll processing costs
- Better compliance with rules and regulations
- Minimal risk of fraud or data leakage
- Lower possibility of errors
Effective from 1st July 2022, the government has introduced some revisions to the basic salary and allowances. As per the new guidelines, the allowances will be capped at a maximum of 50% of the overall package. This rule is set to change the salary component calculation in India.
With the employer’s contribution to PF increasing, the take-home salary is likely to come down. When you decide to go with payroll experts, they can make sure that new regulations like these are followed when creating a salary structure.
Key Takeaways
- A Payroll Structure Focuses on Transparency, Compliance, and Efficiency
- Fixed and Variable Pay Components Drive Stability and Motivation
- The New Wage Code Will Transform Payroll Practices
- Optimized Payroll Systems Enhance Accuracy and Compliance
- Outsourcing Payroll Accelerates Accuracy and Reduces Risk
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is the payroll structure created?
Before creating a salary structure, consider defining the value of every position in your company, analyzing your company’s competitive standing, and also predefining a salary increase rate when compared to market rates. Develop a pay structure based on the information gathered from the market analysis of salary ranges.
2. What are the components of the payroll structure?
The major components of a payroll structure ideally include gross salary, deductions, provident fund, professional tax, Employee State Insurance Corporation, and labor welfare fund.
3. What are the three types of salary structures?
The three types of salary structures are traditional, broadband, and market-based. The most commonly used of the lot is the market-based structure, and broadband is the least used.
4. What constitutes salary in Indian payroll processing?
The two main components that constitute salary in Indian payroll processing are fixed and dynamic or variable. The fixed changes are only on annual revision or based on performance. Dynamic pay is what gets paid on a quarterly, half-yearly, or annual depending on the overall company or department performance.
5. What are the types of payroll systems?
The three types of payroll systems are manual, in-house computerized, and outsourced systems.
6. What Is Payroll Processing Cycle?
Payroll processing is the procedure of calculating and distributing employee salaries that include earnings, taxes, benefits, etc.
7. How Often Should Payroll Records Be Updated or Audited?
Payroll records should ideally be updated when there is a change or modification, like the recruitment of a new hire, a change in employee information, a salary hike, etc.
Contact Us For Business Enquiry

Yugandhara V. M
Yugandhara V. M serves as the Assistant Vice President – HRO at Alp Consulting Ltd., bringing over 14 years of rich experience in Human Resource Outsourcing, payroll management, and statutory compliance. He specializes in driving process excellence across HR operations, ensuring seamless service delivery and compliance with labor laws. Yugandhara’s expertise lies in managing large-scale client engagements, optimizing HR processes, and implementing efficient workforce management systems that enhance organizational performance. He also leads comprehensive payroll services, ensuring accuracy, timeliness, and compliance for diverse client portfolios.




