
Role of HR in Business Strategy: How HR Drives Organisational Success
18/12/2025
The Importance of HRMS Salary Slip For Employers and Employees
18/12/2025- What is Statutory Compliance?
- Why is Statutory Compliance Required?
- Why Is Statutory Compliance Important for Companies and HR?
- What Are the Objectives of Statutory Compliance?
- Who Is Responsible for Statutory Compliance in a Company?
- What are the Key Statutory Compliances for Indian Companies?
- List of Statutory Compliance for Private Limited Company
- What Happens If a Company Fails to Maintain Statutory Compliance?
- What Are the Steps to Ensure Statutory Compliance?
- What Is a Statutory Compliance Checklist for Companies?
- What Are the Best Practices for Managing Statutory Compliance?
- What are the Tips to Stay Compliant and Avoid Penalties in 2026?
- What Are the Latest Statutory Compliance Trends in 2026?
- How Can ALP Consulting Help You Stay Statutorily Compliant?
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Statutory compliance forms the foundation of ethical and lawful business operations in India. It ensures companies function within the country’s legal framework, protecting both employee rights and organizational integrity. From labour laws and taxation to social security contributions like PF and ESI, compliance ensures transparency, accountability, and financial discipline.
Dave Ulrich, a globally respected HR expert, defines statutory compliance meaning as an organization’s responsibility to strictly adhere to government-mandated labour laws, regulations, and statutory obligations.
In 2026, as regulatory landscapes evolve rapidly, businesses must adopt technology-driven compliance management systems to avoid penalties, strengthen governance, and maintain long-term sustainability. Let’s gather deep insights into statutory compliance that will help companies stay ahead.
What is Statutory Compliance?
The pre-defined set of rules within which companies must function in a country is referred to as statutory compliance. These rules are derived from the legal framework in the country. It covers everything from how organizations operate to how they treat their employees. Since there are both state and central laws for statutory compliance, an organization in a state in India must comply with both national-level as well as state-level laws.
Why is Statutory Compliance Required?
Statutory compliance helps ensure that your employees are paid their PF on time, your company files the taxes and other contributions that it makes on behalf of the employee on time, and that employees are paid their health insurance and other policy-related benefits on time.
Without statutory compliance, these things would not happen on time, and you may be under the government’s scanner for evasion of tax and other compliance-related fraud. Several HR consulting companies today not only manage recruitment and payroll but also double up as statutory compliance watchdogs.
Why Is Statutory Compliance Important for Companies and HR?
Statutory compliance is important to the government, the employees in an organization, and the employer. Statutory compliance in HR ensures that employees’ needs are taken care of and whatever is due to them is paid on time.
It helps employers live up to their brand name and the values of honesty and integrity. Statutory compliance in HR helps the government convince the people that they are being well taken care of and will improve its popularity.
What Are the Objectives of Statutory Compliance?
Here are the 5 key objectives of statutory compliance in HR
1. Ensure Legal Adherence
Effective statutory compliance management ensures organizations operate within the framework of applicable laws, preventing legal disputes, penalties, & disruptions to business continuity and reputation.
2. Protect Employee Rights
Statutory compliance safeguards employee interests by ensuring fair wages, benefits, workplace safety, & social security as mandated under various labour and employment laws.
3. Promote Ethical Business Practices
Organisation-wide compliance promotes integrity, transparency, & accountability in operations, strengthening stakeholder trust and fostering a culture of ethical corporate governance.
4. Minimize Financial and Operational Risks
By adhering to statutory obligations, companies can reduce risks of fines, litigation, & financial losses arising from regulatory non-compliance or negligence.
5. Enhance Corporate Reputation and Sustainability
Proper compliance demonstrates responsible governance, builds investor confidence, & boosts brand value, ensuring long-term organizational sustainability and market competitiveness.
Who Is Responsible for Statutory Compliance in a Company?
There are several responsibilities for each of the stakeholders in an organization in statutory compliance. Some of them are:
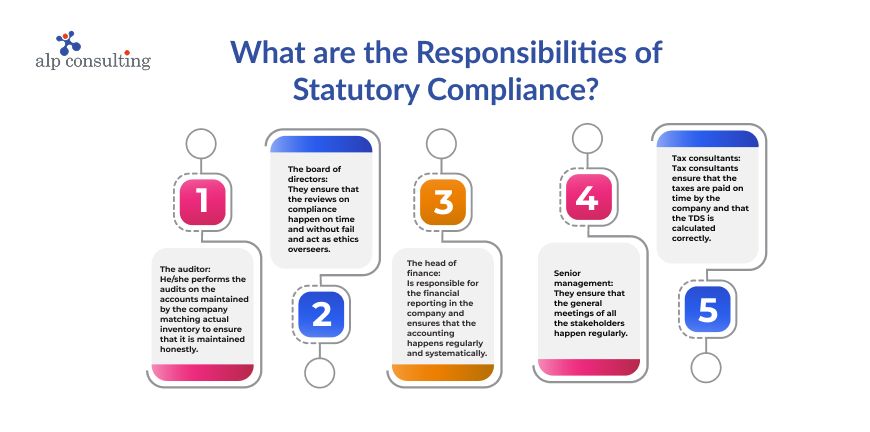
- The auditor: He/she performs the audits on the accounts maintained by the company, matching actual inventory to ensure that it is maintained honestly.
- The board of directors: They ensure that the reviews on compliance happen on time and without fail, and act as ethics overseers.
- The head of finance is responsible for the financial reporting in the company and ensures that the accounting happens regularly and systematically.
- Senior management: They ensure that the general meetings of all the stakeholders happen regularly.
- Tax consultants: Tax consultants ensure that the taxes are paid on time by the company and that the TDS is calculated correctly.
What are the Key Statutory Compliances for Indian Companies?
Employers must contribute towards the maintenance of statutory compliance. They must ensure that compliance happens regularly and that it is not a one-time thing. A list of statutory compliance practices to be followed mandatorily by companies in India is mentioned below:
1. Holding board meetings
The members of the board must meet at least four times a year, with the gap between two board meetings not exceeding 120 days.
2. Appointing an auditor
A chartered accountant must be appointed as the auditor of the company within a time frame of 30 days from the incorporation of the company.
3. Yearly general meetings
There must be general meetings held every year to discuss issues related to compliance and the concerns of employees.
4. Issuing a share certificate
According to the Companies Act, a company must issue its share certificate within two months of its incorporation of the company.
5. Recording the minutes of meetings
Meeting minutes must be recorded by the company secretary in a very faithful manner to keep track of and for a consensus on issues.
6. Maintaining a book of accounts
A company, whether it is public, private, or private limited, must maintain a book of accounts to ensure that its statutory compliance is on track.
7. Auditing the book of accounts
A company must carry out an audit every year they are exempt from it by employing an expert and qualified auditor.
8. Circulating financial reports
The financial reports of the company must be circulated every year so that there is transparency regarding the financial transactions made by the company.
9. Filing forms with the Registrar of Companies
Certain forms must be filed with the Registrar of Companies. The forms to be filed depend on the state in which the company is to.
10. Maintaining statutory registers
Statutory registers must be maintained, which include members’ registers, board of directors registers, and registers of duplicate or renewed share certificates.
As the company grows in size, PF, attendance, labor law adherence, etc., must also be maintained by the company.
List of Statutory Compliance for Private Limited Company
1. Board Meeting
A board meeting must happen every 120 days at least. There must be at least 4 meetings a year, regardless of the type of company.
2. General Meeting (AGM)
An annual general meeting must be convened within 6 months of the financial reporting of the company.
3. Appointment of an Auditor
An auditor must be appointed within 30 days of the registration of the company.
4. Director Disclosure
A full disclosure must be made of all the directors associated with the company.
5. Accounts to be Audited
This must happen within six months of the end of the financial year.
6. Filing of form MGT-7
The MGT-7 form must be filed within 60 days of the annual general meeting, which must be held at the end of the financial year.
7. Filing of Financial Statement (Form AOC-4)
The financial statement must be filed by the company every financial year with the Registrar of Companies.
8. Maintenance of Statutory Registers
Statutory registers, as mentioned earlier, must be maintained for a private limited company too.
What Happens If a Company Fails to Maintain Statutory Compliance?
Here are 5 negative consequences of failing to maintain statutory compliance:
1. Financial Penalties
Compliance violations can lead to substantial fines, late fees, & interest charges, significantly affecting the company’s financial stability and profitability.
2. Legal Actions and Prosecution
Authorities may initiate legal proceedings, resulting in court cases, criminal charges, or imprisonment of responsible directors & officers.
3. Loss of Business License
Repeated compliance offences can lead to suspension or cancellation of operating licenses, halting business operations entirely.
4. Reputational Damage
Failure to comply damages brand credibility, erodes stakeholder trust, & negatively impacts customer and investor confidence.
5. Disruption of Business Operations
Regulatory interventions and investigations can disrupt day-to-day operations, delay projects, & reduce overall business productivity and efficiency.
What Are the Steps to Ensure Statutory Compliance?
When the government passes a law, it wants to ensure that companies do certain things.
Whether it is ensuring safety standards or promoting waste management, there are many ways you can ensure statutory compliance in business. Here’s how:
1. Details of Statute and Regulations
Ensure your organization has all the required details of the statute and regulations. This includes:
a) The name of the statute, regulation, or code that applies to your organization.
b) The date on which the law was passed or enacted.
c) The authority under which it was passed or enacted.
d) The format in which it is written (legislative-type or executive-type).
e) A description of how your business will comply with this law (e.g., what activities you need to perform).
2. Understanding of Legal Responsibilities
Ensure that employees understand their legal responsibilities, rights, obligations, and liabilities due to their actions (if any). This can be done through training programs, education materials, etc.
What Is a Statutory Compliance Checklist for Companies?
Here are 20 checklist aspects companies must satisfy to ensure statutory compliance management remains on the right track:
1. Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
Companies must ensure timely EPF registration, monthly contributions, employee records maintenance, & submission of returns to the EPFO portal accurately.
2. Employees’ State Insurance (ESI)
The HR team must register eligible employees, deposit their ESI contributions before due dates, and file periodic returns to maintain employee health benefits.
3. Professional Tax
The finance team must deduct professional tax from employee salaries as per state laws, remit payments promptly, & maintain proper transaction records.
4. Labour Welfare Fund (LWF)
Contribute employer and employee portions to the Labour Welfare Fund and file periodic returns with the respective state authorities.
5. Minimum Wages Act
Ensure employees are paid not less than the government-notified minimum salary applicable to their job category and region.
6. Payment of Wages Act
Disburse employee net salaries timely, maintain payment records, & ensure lawful deductions as defined under relevant statutory provisions.
7. Gratuity Act
Register under the Payment of Gratuity Act, calculate gratuity eligibility correctly, & pay employees upon retirement or resignation( 5 years’ service needed for eligibility).
8. Shops and Establishments Act
Employers must obtain registration, renew licenses periodically, display mandatory notices, and follow state-specific working hours and leave regulations strictly.
9. Factories Act Compliance
The management must ensure factory registration, employee safety, working conditions, welfare measures, and maintain inspection records per statutory requirements.
10. Payment of Bonus Act
Calculate and distribute annual bonuses to eligible employees based on prescribed wage limits and maintain distribution records.
11. Equal Remuneration Act
Ensure fair wages without gender discrimination, maintain employment records, and promote equality in recruitment and promotion practices.
12. Maternity Benefit Act
Provide eligible female employees with maternity leave, benefits, and safeguards against termination during pregnancy or maternity leave.
13. Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace Act
Form the Internal Complaints Committee (ICC), conduct regular awareness sessions, and ensure a safe, respectful workplace environment for all employees.
14. Contract Labour (Regulation & Abolition) Act
Register principal employer, verify contractor licenses, maintain attendance, and ensure equal pay and facilities for contract workers.
15. Income Tax
Deduct TDS accurately from employee salaries, file quarterly returns, issue Form-16, and remit taxes before due dates.
16. Goods and Services Tax (GST)
Register under GST, issue compliant invoices, file monthly/annual returns, and pay taxes within specified timelines.
17. Companies Act
Maintain statutory registers, conduct board meetings, file annual returns, and comply with auditing, financial disclosure, and director requirements.
18. Environmental and Pollution Control
Obtain necessary clearances, follow waste management guidelines, monitor emissions, and submit reports to the Pollution Control Board regularly.
19. Employee State Labour Law Posters Display
Display statutory compliance posters and abstracts at the workplace as per the central and state labour law mandates.
20. Annual Statutory Audit
Conduct internal and external audits annually, review compliance gaps, and ensure timely rectification of identified statutory issues.
What Are the Best Practices for Managing Statutory Compliance?
Here are the 5 best practices for effective statutory compliance management:
1. Implement a Centralized Compliance Management System
Adopt digital compliance software to track deadlines, automate filings, & store legal documents securely, ensuring transparency, accountability, & timely adherence across all departments and locations.
2. Conduct Regular Internal Audits and Compliance Reviews
Schedule periodic compliance audits to identify gaps, verify documentation accuracy, and ensure all statutory obligations are met before government inspections or legal evaluations occur.
3. Provide Continuous Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Educate employees regarding relevant laws, policy updates, and compliance responsibilities via regular interactive training sessions, ensuring organizational alignment & minimizing human errors in regulatory reporting.
4. Engage Expert Legal and Compliance Advisors
Collaborate with experienced consultants or outsourced compliance officers to interpret evolving regulations, mitigate risks, and maintain an up-to-date understanding of complex statutory requirements.
5. Maintain Transparent Documentation and Reporting Mechanisms
Keep clear, accessible records of filings, licenses, & audits, ensuring proper documentation trails for easy verification during inspections and fostering a culture of compliance and integrity.
What are the Tips to Stay Compliant and Avoid Penalties in 2026?
Here are 5 tips to stay compliant and prevent penalties in 2026:
1. Stay Updated with Regulatory Changes
Regularly monitor government notifications, amendments, and circulars to stay informed about new compliance requirements & adapt company policies accordingly to avoid penalties.
2. Automate Compliance Tracking and Reporting
Use AI-powered compliance software to schedule reminders, file returns automatically, & generate real-time reports, ensuring no deadlines or statutory obligations are missed.
3. Conduct Periodic Compliance Health Checks
Perform quarterly internal audits to assess compliance readiness, identify potential risks, & implement corrective measures before government inspections or enforcement actions occur.
4. Strengthen Interdepartmental Coordination
Encourage collaboration between HR, finance, & legal teams to ensure unified compliance efforts, accurate documentation, & consistent adherence across all regulatory domains.
5. Partner with Expert Compliance Consultants
Engage professional compliance service providers like Alp Consulting to manage complex statutory filings, interpret evolving laws, and ensure full adherence to 2026’s regulatory environment efficiently.
What Are the Latest Statutory Compliance Trends in 2026?
Here are 5 latest statutory compliance trends in 2026
1. AI-Driven Compliance Monitoring
Artificial intelligence automates compliance tracking, detects irregularities early, & predicts potential risks using real-time regulatory data analytics.
2. Cloud-Based Compliance Platforms
Organizations adopt cloud systems for centralized data management, real-time collaboration, & improved transparency in statutory reporting processes.
3. ESG-Linked Compliance Reporting
Companies integrate environmental, social, & governance (ESG) metrics into compliance frameworks to meet global sustainability and transparency standards.
4. Real-Time Regulatory Updates Integration
Automated compliance software now syncs directly with government databases, providing instant alerts on rule changes and filing deadlines.
5. Enhanced Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Compliance
Tightened data protection laws demand stronger cybersecurity measures, encrypted documentation, & strict adherence to digital compliance protocols globally.
How Can ALP Consulting Help You Stay Statutorily Compliant?
At Alp Consulting, we simplify statutory compliance by offering end-to-end solutions that keep your business legally secure & penalty-free. Our experts ensure timely filings, accurate documentation, and adherence to all labour, tax, and regulatory laws across India.
With advanced compliance automation, real-time monitoring, and customized advisory support, we help businesses reduce risks and maintain transparency. Whether it’s PF, ESI, GST, or payroll compliance, we ensure seamless operations and peace of mind through proactive, technology-driven statutory management.
Conclusion
In 2026’s evolving regulatory landscape, staying compliant is not optional: it’s essential for business stability & reputation. Statutory compliance ensures transparency, employee protection, and sustained growth while minimizing financial and legal risks.
At Alp Consulting, we simplify complex compliance obligations through technology-driven solutions, expert guidance, and proactive monitoring. From PF and ESI to tax and labour law compliance, our tailored services keep your business penalty-free and future-ready.
Partner with Alp Consulting today to simplify compliance, strengthen trust, and ensure peace of mind.
Talk today to Alp Consulting to get your statutory compliance in order.
Key Takeaways
- Statutory compliance ensures businesses adhere to essential labour, tax, and regulatory frameworks in India.
- Non-compliance can result in heavy financial penalties, legal actions, and severe reputational damage.
- Automation and AI-based tools are transforming compliance tracking, monitoring, and documentation accuracy.
- Regular audits, employee training, and transparent reporting strengthen organizational compliance culture.
Partnering with expert compliance consultants ensures efficiency, risk mitigation, and long-term business sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What Is the Difference Between Statutory Compliance and Regulatory Compliance?
Statutory compliance in HR follows government-mandated laws, while regulatory compliance adheres to industry-specific rules set by professional or governing bodies.
2. How Often Should a Company Review Its Statutory Compliance Status?
Companies should review statutory compliance quarterly or biannually to ensure adherence to new laws & regulatory updates.
3. Can Statutory Compliance Be Automated?
Yes, compliance automation tools streamline tracking, documentation, and reporting, reducing manual errors and ensuring timely statutory filings.
4. What Are the Consequences of Failing Statutory Compliance in India?
Non-compliance with statutory regulations leads to heavy fines, penalties, reputational loss, legal action, and in severe cases, suspension of business operations.
5. Does Statutory Compliance Differ From State to State in India?
Yes, statutory compliance differs across states due to region-specific labour laws, taxation rules, & local government regulations.
6. How Can an Organization Build a Culture of Compliance?
Organizations can foster a compliance culture via leadership commitment, continuous employee training, transparent communication, and regular internal audits.
Contact Us For Business Enquiry

Hariharan Iyer
Hariharan Iyer is the Vice President – Operations at ALP Consulting, bringing over 40+ years of experience in HR outsourcing and labour law compliance. He leads end-to-end HRO operations, ensuring process efficiency, statutory compliance, and seamless service delivery for clients across industries. With a strong background in labour law governance and workforce management, Hariharan plays a key role in driving operational excellence and compliance-led HR solutions at ALP Consulting.





