
What are the Different Types of Payroll Deductions?
24/02/2025
Top 10 HR (Human Resource) Outsourcing Companies in India
24/02/2025Building a future-ready workforce is easier than it seemed to be a decade ago. With the introduction of both NAPS and NATS apprenticeship programs in this decade, there is a light down the path, but the path to be chosen must be well-defined too. In this article, we look at the other government initiatives that will help build a well-defined path forward to a future-ready workforce in India.
Skill Development Strategy for Productivity, Employment and Sustainable Development
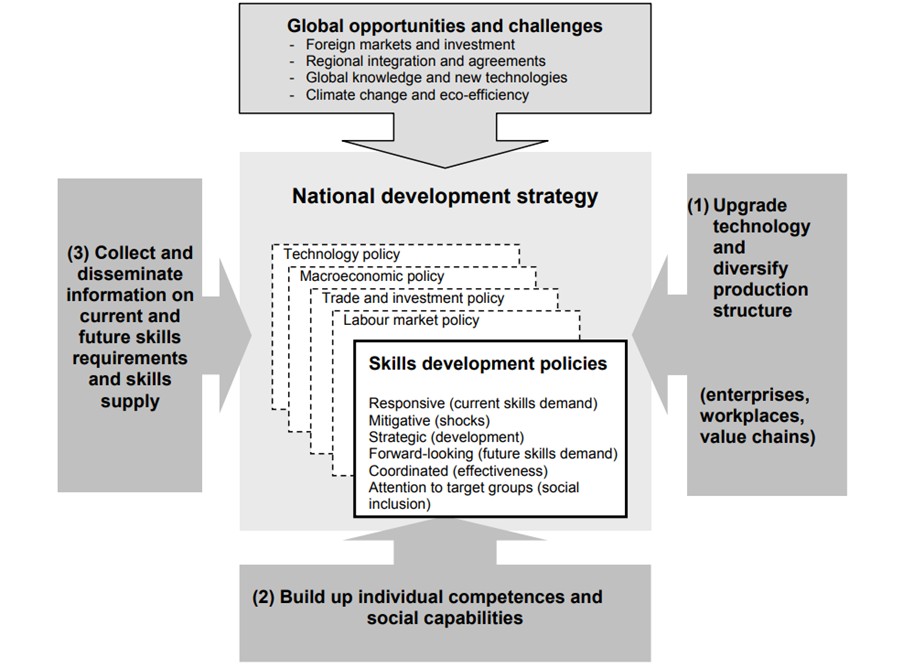
Beginning with a Trusted Strategy
The above diagram outlines a strategy for developing a workforce for the future in a country through skill development, technology upgrades, and the collection of information on current and future skill requirements in the country. The state of foreign markets, climate change, and eco-consciousness also contribute in a big way to developing the strategy. It was proposed by the International Labor Organization (ILO).
In this article, we will be analyzing the stance taken by the Indian Government towards skill development within the purview of the diagram above. We will be looking at what initiatives the government is taking, describing how they are proceeding with it, and then going back to how it all fits in with the plan laid out by ILO for a nation to achieve skill development to build a future-ready workforce.
Government-Mediated Steps Towards Sustainable Employment in the Future
1. Partnership with the Private Sector Through Apprenticeship
Partnering with the private sector by actively offering apprenticeship and industry exposure programs for students is the way forward. The government has instituted the NAPS program, encouraging private institutions to appoint apprentices, who will be paid a lower salary by the company with a stipend awarded by the government.
They will be trained by authorized training partners, and the business also need not offer the apprentices any of the benefits they offer their regular employees. This allows startups to acquire talent (they can train) at a much lower cost and helps the business get them future ready. This is an example of a mitigative strategy towards skill development as per the diagram.
2. Collaboration Between Educational Institutions and Industries
Enhancing collaboration between educational institutions and industries can help align future generations with the future demands of industry. To achieve this, India is working with educational institutions to develop curricula aligned with the needs of different industries.
India is also promoting industry guest lectures, workshops and industry-institute partnerships which provide internship opportunities for graduates and diploma holders. This is an example of a well-coordinated and forward-looking skill development plan.
3. Boosting Learning Opportunities with MOOCS and Technology
Making online learning platforms and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) (digital platforms) enables the spread of skilling opportunities to a wider population empowered by technology. An example of such a large online learning platform with MOOCs launched by the government is SWAYAM.
Developed by AICTE in 2016, SWAYAM wants to bridge the digital divide and provide access to quality learning and teaching resources for everyone. Another example of a government–developed MOOC is the ePGPathshala. Both types of skill development are strategic and responsive.
4. Career Counselling and Guidance from Secondary Schools
Set up career counseling and guidance in secondary schools providing the necessary exposure to students to vocational education at an early age. The focus on developing both technical and vocational skills is unique under the National Education Policy (NEP) program for schools.
Personalized career counselling is provided to all the students to pick the desired pathways as per their unique interests and abilities. There is a huge demand for jobs in semiconductor and energy industries and proper counselling can help identify suitable talent. This is an example of both strategic as well as responsive skill development.
5. Encourage Entrepreneurship and Innovation through Technology and Active Facilitation
Encouraging entrepreneurship and innovation will help foster a culture of job creation and employment not only for one but for everyone else too. The government wants to develop more industrial corridors and smart cities. The ones that have already been developed will have high-speed communication access and integrated logistics arrangements.
The government has also identified 25 sectors for entrepreneurship. The government will also act as a facilitator rather than just a regulator. Together, these aspects will help kindle the spirit of entrepreneurship.
6. Integration of Distance and Regular Education to Give Diverse People a Chance
The integration of both distance and regular education in several government and private institutes is another step in the right direction and provides flexibility and wider access to learners from diverse backgrounds, bridging the knowledge gaps and allowing people from all skill levels to share in the progress of our beautiful, populous and diverse country. This type of skill development is the targeted type of skill development as defined in the diagram.
Closing Words
In the new age of AI, the Metaverse, 5G, IoT, AR, VR, and other allied technologies, it is important that the government prioritizes the use of these advanced technologies to also strengthen the skill levels and prompt continuous learning to build a future-ready workforce. An example would be the use of Generative AI to build a function for a musical fountain (rather than a simple fountain) that changes with the song.
Or that of using AR and VR to navigate complex concepts by placing the subject in the world. Finally, it is not necessary that the talent the nation is proud of starts out as a graduate skill ready for the workplace. She/He may be an apprentice too, continuously learning at work and upskilling oneself the hard way. Also, learning never really stops, with there being great leaps in technological advancement. The youth of India need to ready themselves for newer and more evolved jobs because the future might already be here.
Contact Us For Business Enquiry

Rajkumar Shanmugam
Rajkumar Shanmugam is the Head of HR at ALP Consulting, bringing over 19 years of comprehensive HR leadership experience across India and international markets. His expertise spans talent acquisition, employee relations, performance management, compliance, and HR transformation. Rajkumar has a proven track record of driving people-centric initiatives, enhancing workplace culture, and aligning HR strategy with business goals. With extensive experience in US staffing operations and global mobility, he continues to lead organizational excellence through innovation and employee engagement.




